Table of contents:
High-Voltage Transformer for Grid Protection
High-voltage networks cannot run safely and efficiently without reliable high-voltage transformers that allow electricity from power plants to be stepped up for transmission and then brought down again for distribution and everyday use. Since not all transformers are built the same, to choose the right one it is necessary to consider several factors. This means things like the environment it will operate in, the design specifications, and the needs of the whole system. Let’s explore what high-voltage transformers do, their main types, and what to keep in mind when deciding which one fits a particular application.

Introduction to High-Voltage Transformers
A high voltage transformer is a critical grid component that changes the voltage to safe and usable secondary voltage value which is compatible with the distribution infrastructure. Its basic function is the protection of both the energy system and the users. High-voltage transformers are found in power plants, substations, and transmission lines.
Depending on their features, they might be considered as step down transformers (giving back energy to the distribution network at medium or low voltage from high voltage transmission) or as instrument transformers for measurement and protection only. In any case, a proper transformer will be the key to the successful passage of AC voltage, as well as the stable performance of the device under heavy conditions, such as short-circuit currents, switching surges or load variations.
High-Voltage Transformer Types
Depending on the application, several categories of high-voltage transformers are available, each with its own set of features and characteristics. Usually, the specific types also serve different roles within the grid.
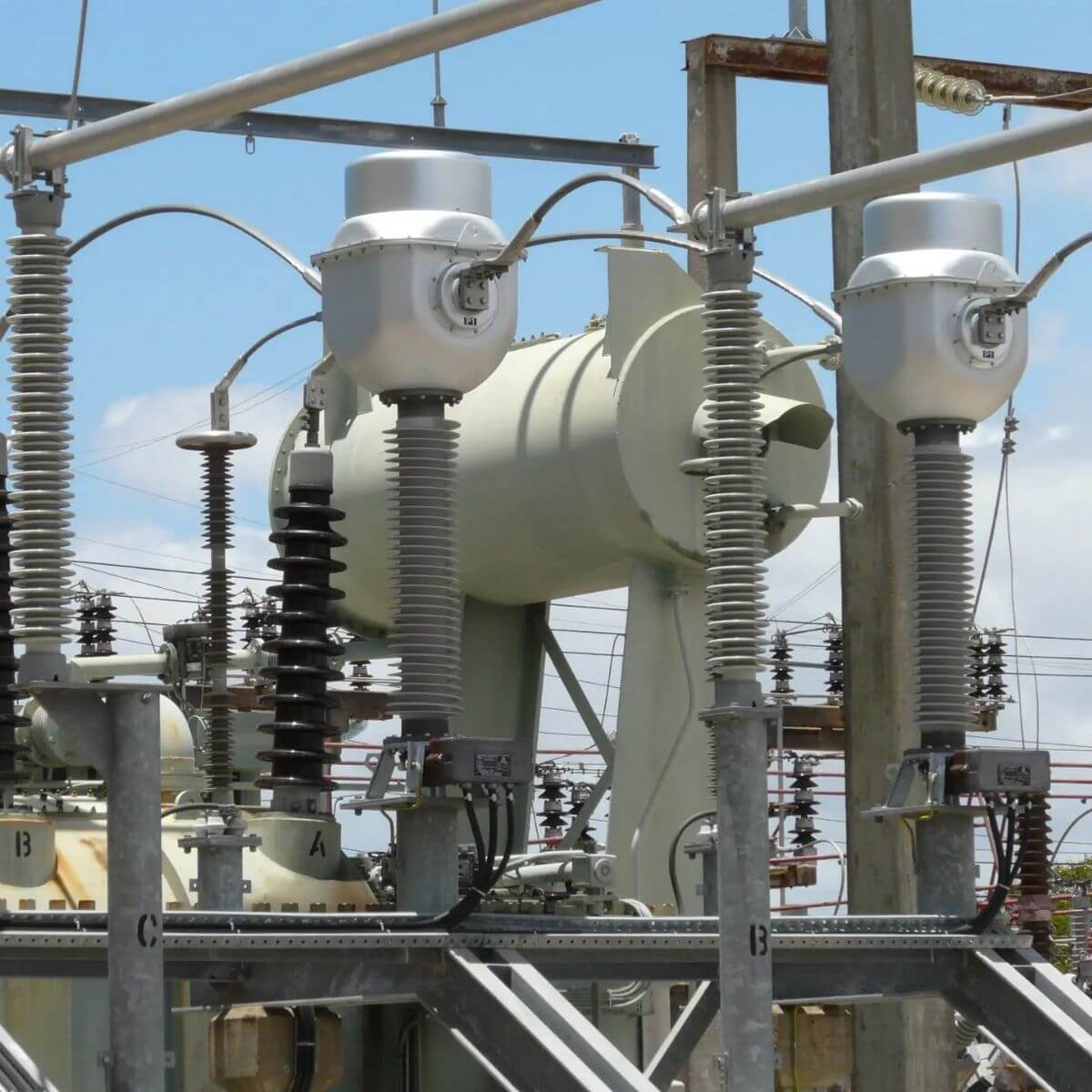
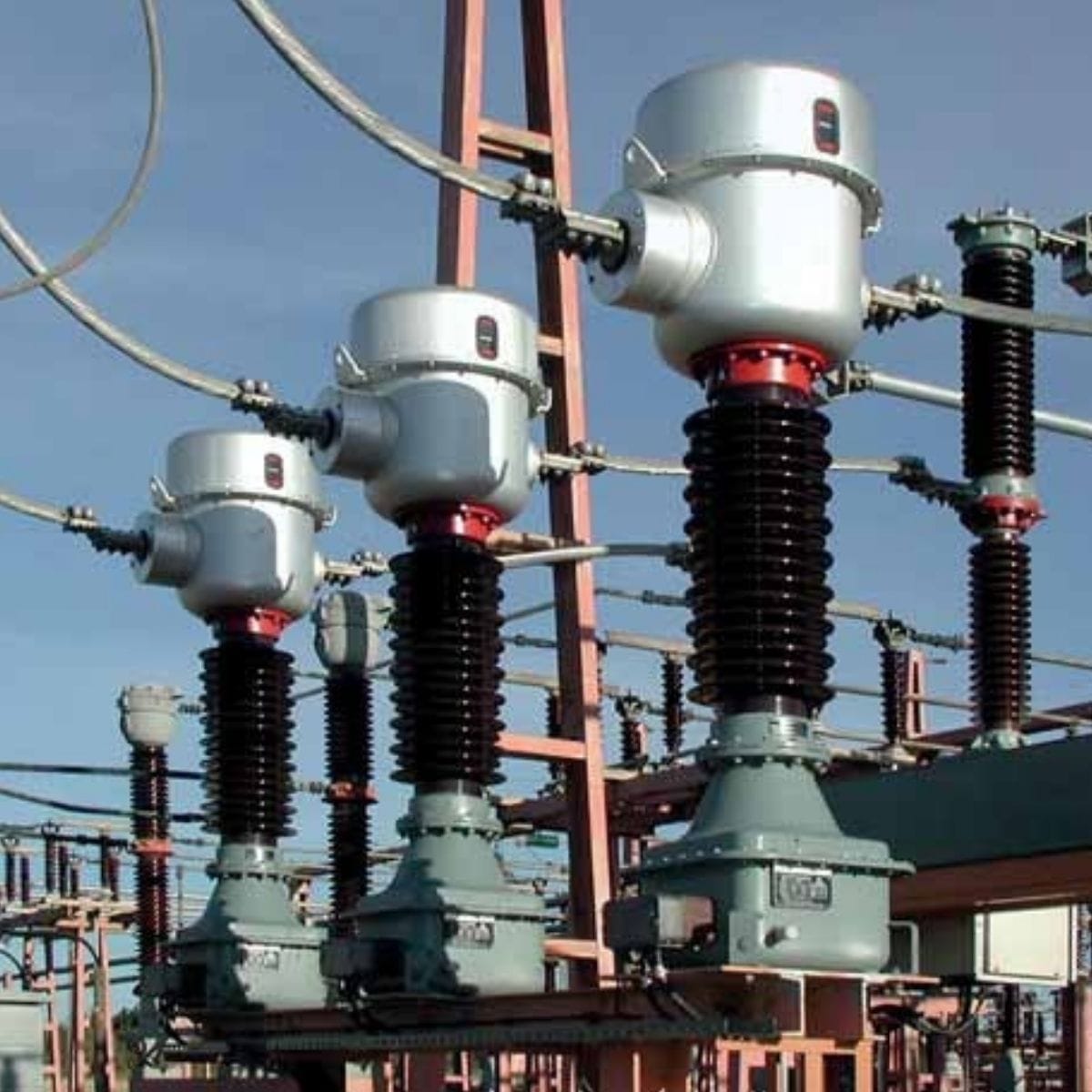
- Current Transformers (CTs) – they are designed to measure and monitor current flow in power systems, which allows safe metering and relay protection. Available as units in paper-oil insulation for voltages between 72.5 kV and 765 kV.
- Voltage Transformers (VTs) – they convert (step down) primary voltage to a standardized secondary voltage suitable for instruments and protection devices. Commonly used in substations and distribution networks. Available for voltages between 72.5 kV and 525 kV.
- Optical Current Transformers (OCTs) – they are a more advanced variation of the regular current transformer that uses fiber-optic technology for precise current measurement. These are immune to electromagnetic interference and ideal for digital substations. Available for voltages between 145 kV and 550 kV.
- Combined Transformers – they integrate the functions of CTs and VTs in one unit, reducing space requirements and installation costs. Typically used in network transformers. Available for voltages between 72.5 kV and 300 kV.
- Auxiliary Transformers (SSVT) – they are dedicated to feeding control systems, relays, and auxiliary equipment in HV substations. Available for voltages between 72.5 kV and 550 kV.
While their specifications vary, all transformer types described above are pretty similar in terms of how they are made (and what they are constructed of).

High-Voltage Transformer Design and Materials
The design of a high-voltage transformer must ensure reliability, long service life, and maximum resistance to environmental factors. Depending on the product range, Protektel’s products employ various construction approaches and solutions.
- Paper-Oil Insulation – using insulating oil to cool and protect the transformer’s primary and secondary windings, ensuring durability at high voltage levels. This approach is widely used in current transformers and voltage transformers, with ratings of up to 765 kV.
- Composite and Silicone Insulation – they provide excellent resistance to weather, pollution, and humidity, extending operational reliability of a voltage transformer.
- Optical Technology – implemented in SDO-OCT optical current transformers, it eliminates the need for traditional iron-core designs, offering high precision and immunity to electromagnetic disturbances.
- Robust Windings and Cores – optimized for stable performance under varying loads, whether dealing with AC or DC voltage conversion needs.
By combining proven insulation materials with innovative protection and measurement technologies, Protektel ensures its instrument transformers meet the highest requirements. This way they are able to provide accuracy, safety, and performance in demanding HV environments.
How to Choose the Appropriate High-Voltage Transformer?
Choosing the right transformer for a specific project is dependent on multiple factors that must align with system requirements. Before deciding on the equipment choice, it’s worth considering the following criteria.
- Voltage rating – the rated primary voltage and expected secondary voltage must match the system’s operating conditions. For measurement transformers, accuracy at both nominal and fault levels is crucial.
- Application type – whether the unit is required for metering, protection, auxiliary supply, or voltage transformation in a distribution system or power plant.
- Load and output voltage – consideration of the required output voltage, secondary windings capacity, and expected operating loads.
- Environmental conditions – pollution levels, humidity, altitude, and temperature range determine the choice of insulation and housing materials.
- System configuration – the role of the transformer within primary and secondary sides of the network, including grounding practices and the presence of switching surges.
By evaluating these factors, grid operators can ensure reliable functioning, extended service life, and minimized risk of power outages.

Summary
High-voltage transformers play a central role in modern power systems. They convert voltages to levels suitable for distribution while maintaining stable and reliable operation. Whether used as step-down transformers, instrument transformers, or optical current transformers, HV transformers are meant to ensure accurate measurement, effective protection, and consistent performance across the network.
Protektel range of high-voltage transformer solutions is designed to meet specific operational requirements. From oil-immersed CTs and VTs to optical and combined transformers, our equipment is engineered for reliability, even under the most demanding conditions.
Evaluating options for a project? Reach out to our team – we can guide you through the portfolio and help identify the transformer that best fits your system’s needs.